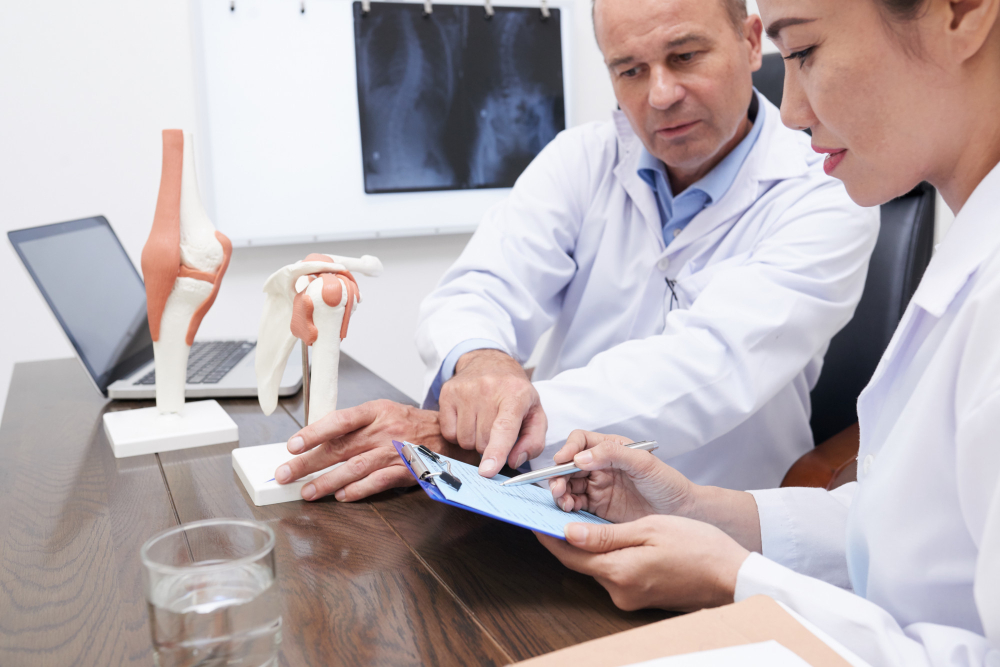
Cartilage transplantation is a modern solution for people with joint pain or injury. Many people seek cartilage repair surgery to restore movement and reduce pain. In fact, joint cartilage restoration can help you return to daily activities. If you live in a busy city, orthopedic cartilage treatment may be available near you. This guide explains what cartilage transplantation is, who needs it, and how it helps.
What is Cartilage Transplantation?
Cartilage is a smooth tissue that covers the ends of bones in your joints. It helps your joints move easily. However, when cartilage gets damaged, it cannot heal on its own. Cartilage transplantation is a surgery that replaces damaged cartilage with healthy tissue. Sometimes, doctors use your own cartilage. Other times, they use donor tissue. This treatment aims to restore joint function and reduce pain.
Who Needs Cartilage Transplantation?
Not everyone with joint pain needs this surgery. However, some people benefit more than others. You may need cartilage transplantation if:
On the other hand, people with severe arthritis may need other treatments. Always talk to a doctor to see if this surgery is right for you.
Common Symptoms and Causes of Cartilage Damage
Cartilage damage can happen for many reasons. Often, it leads to pain and swelling. Common symptoms include:
There are several causes of cartilage damage. For example, you may injure your joint during sports. Sometimes, a fall or accident can harm cartilage. In addition, wear and tear over time can also cause damage. Obesity and joint diseases may increase your risk as well.
How is Cartilage Transplantation Diagnosed?
Doctors use several steps to diagnose cartilage damage. First, they ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they examine your joint for pain, swelling, or movement problems. Then, they may order imaging tests, such as:
Sometimes, doctors use a small camera called an arthroscope to look inside the joint. This helps them see the damage clearly. Early diagnosis can lead to better results after surgery.
Treatment Options and Surgical Procedures
Doctors offer several treatments for cartilage damage. Sometimes, simple treatments like rest, physical therapy, or medicine help. However, if these do not work, surgery may be needed. Common cartilage transplantation procedures include:
Your doctor will choose the best option based on your age, activity level, and joint condition.
Recovery and Lifestyle Guidance After Surgery
After cartilage transplantation, recovery takes time. However, following your doctor’s advice helps you heal faster. Here are some tips for recovery:
Most people return to normal activities in a few months. Still, full recovery may take up to a year. Eating healthy foods and staying at a healthy weight can also help your joints heal.
Prevention Tips for Joint Health
While not all cartilage damage can be prevented, you can lower your risk. Consider these tips:
Early care can prevent further damage and keep your joints healthy.
In summary, cartilage transplantation offers hope for people with joint pain or injury. If you think you may benefit from cartilage repair surgery, consult an orthopedic specialist at Sri Lakshmi Hospital to discuss if cartilage transplantation is right for you.